122 Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
Say you have an array for which thei_thelement is the price of a given stock on day_i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you like (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times).
Note:You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
Example 1:
Input:
[7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output:
7
Explanation:
Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
Example 2:
Input:
[1,2,3,4,5]
Output:
4
Explanation:
Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Note that you cannot buy on day 1, buy on day 2 and sell them later, as you are
engaging multiple transactions at the same time. You must sell before buying again.
Example 3:
Input:
[7,6,4,3,1]
Output:
0
Explanation:
In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if (prices == null) {
return 0;
}
if (prices.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
profit += (prices[i] - prices[i - 1]); //greedy
}
}
return profit;
}
}
Algorithm
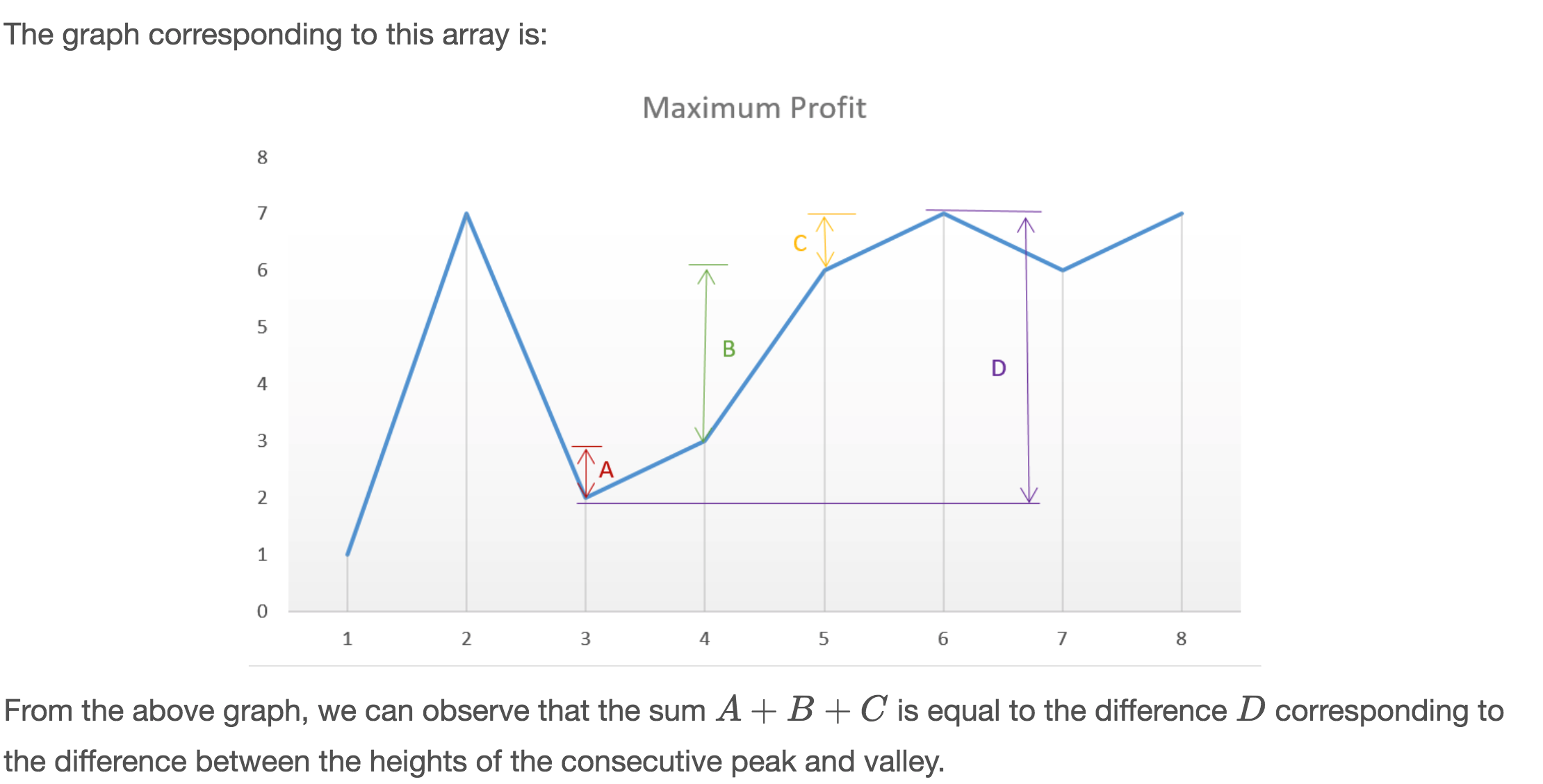
This solution follows the logic used in Approach 2 itself, but with only a slight variation. In this case, instead of looking for every peak following a valley, we can simply go on crawling over the slope and keep on adding the profit obtained from every consecutive transaction. In the end,we will be using the peaks and valleys effectively, but we need not track the costs corresponding to the peaks and valleys along with the maximum profit, but we can directly keep on adding the difference between the consecutive numbers of the array if the second number is larger than the first one, and at the total sum we obtain will be the maximum profit. This approach will simplify the solution. This can be made clearer by taking this example:
[1, 7, 2, 3, 6, 7, 6, 7]
 Complexity Analysis
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity :O(n)O(n). Single pass.
Space complexity:O(1)O(1). Constant space needed.