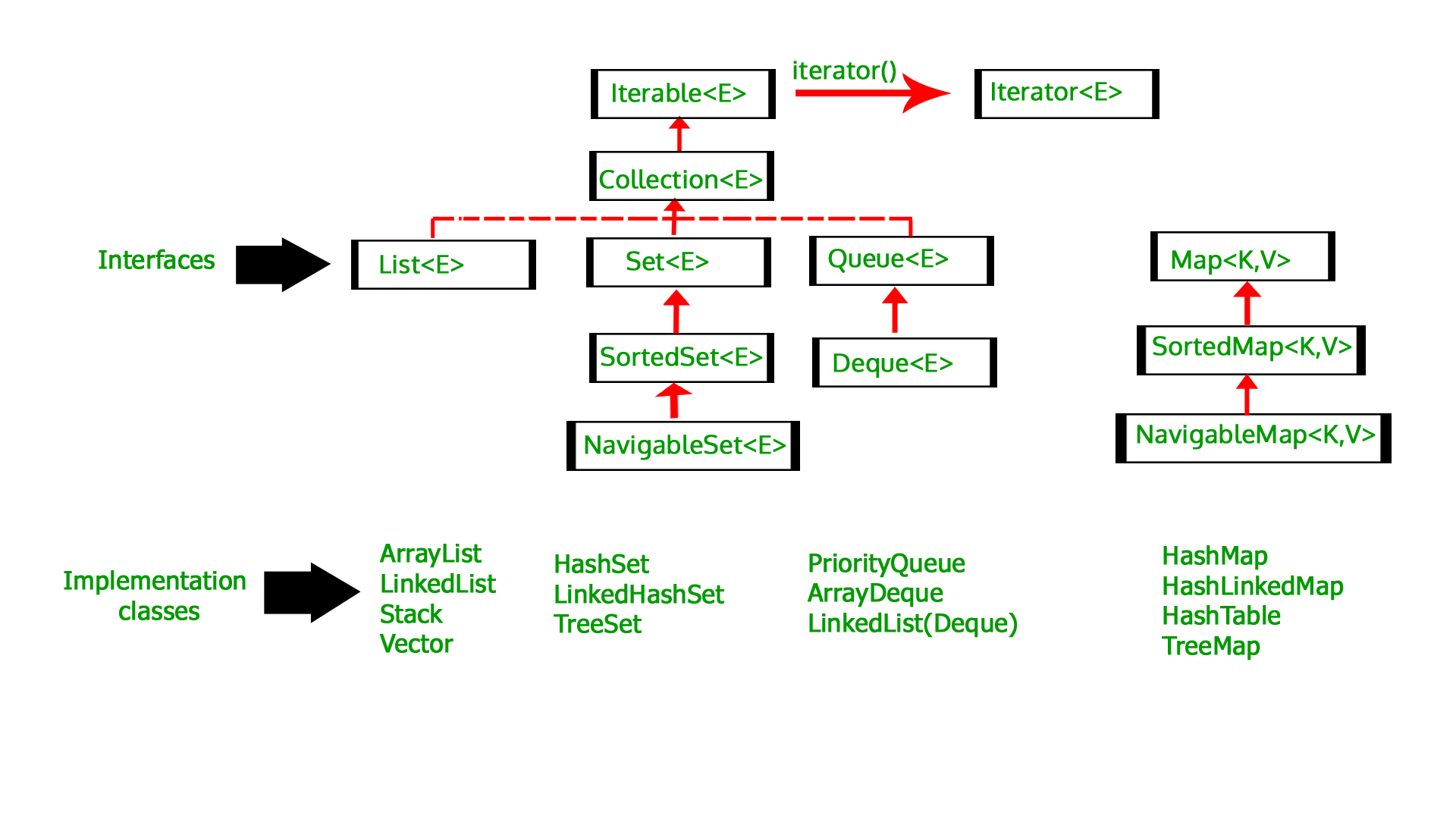
The java.util.Deque interface is a subtype of thejava.util.Queue interface. The Deque is related to the double-ended queue that supports addition or removal of elements from either end of the data structure, it can be used as aqueue (first-in-first-out/FIFO)or as astack (last-in-first-out/LIFO).
Methodsof deque:
- add(element): Adds an element to the tail.
- addFirst(element): Adds an element to the head.
- addLast(element): Adds an element to the tail.
- offer(element): Adds an element to the tail and returns a boolean to explain if the insertion was successful.
- offerFirst(element): Adds an element to the head and returns a boolean to explain if the insertion was successful.
- offerLast(element): Adds an element to the tail and returns a boolean to explain if the insertion was successful.
- iterator(): Returna an iterator for this deque.
- descendingIterator(): Returns an iterator that has the reverse order for this deque.
- push(element): Adds an element to the head.
- pop(element): Removes an element from the head and returns it.
- removeFirst(): Removes the element at the head.
- removeLast(): Removes the element at the tail.
Deque deque = new LinkedList<>();
// We can add elements to the queue in various ways
deque.add("Element 1 (Tail)"); // add to tail
deque.addFirst("Element 2 (Head)");
deque.addLast("Element 3 (Tail)");
deque.push("Element 4 (Head)"); //add to head
deque.offer("Element 5 (Tail)");
deque.offerFirst("Element 6 (Head)");
deque.offerLast("Element 7 (Tail)");
System.out.println(deque + "\n");
// Iterate through the queue elements.
System.out.println("Standard Iterator");
Iterator iterator = deque.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
System.out.println("\t" + iterator.next());
// Reverse order iterator
Iterator reverse = deque.descendingIterator();
System.out.println("Reverse Iterator");
while (reverse.hasNext())
System.out.println("\t" + reverse.next());
// Peek returns the head, without deleting
// it from the deque
System.out.println("Peek " + deque.peek());
System.out.println("After peek: " + deque);
// Pop returns the head, and removes it from
// the deque
System.out.println("Pop " + deque.pop());
System.out.println("After pop: " + deque);
// We can check if a specific element exists
// in the deque
System.out.println("Contains element 3: " +
deque.contains("Element 3 (Tail)"));
// We can remove the first / last element.
deque.removeFirst();
deque.removeLast();
System.out.println("Deque after removing " +
"first and last: " + deque);